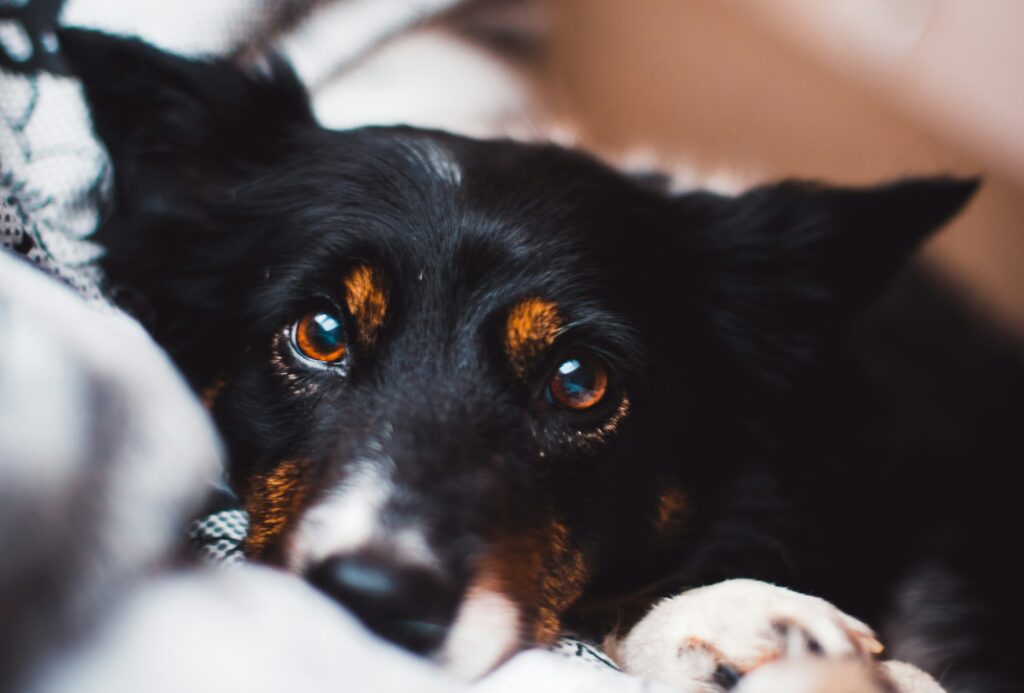
The eyes are windows to the soul, reflecting the health and well-being of our canine companions. Dogs, with their keen sense of sight, rely heavily on their eyes to navigate the world around them. However, like humans, dogs can experience various eye problems that may affect their vision and overall ocular health. As a responsible dog owner, it’s crucial to be vigilant in recognizing signs of eye issues and to understand the appropriate steps for treatment. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore common eye problems in dogs, shed light on their causes, and provide insights into effective treatment strategies.
Identifying Common Eye Problems in Dogs
- Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye): Conjunctivitis is characterized by inflammation of the conjunctiva, the membrane lining the eyelids and covering the eyeball. Symptoms include redness, discharge, and increased tearing. Allergies, infections, or irritants can trigger conjunctivitis in dogs.
- Corneal Ulcers: Corneal ulcers are abrasions on the surface of the cornea, often caused by trauma or foreign objects. Signs include squinting, excessive tearing, and sensitivity to light. Corneal ulcers require immediate veterinary attention to prevent complications.
- Cherry Eye (Protruding Third Eyelid Gland): Cherry eye occurs when the gland in the third eyelid protrudes, leading to a reddish mass resembling a cherry. While not usually painful, it can cause irritation and requires surgical correction.
- Cataracts: Cataracts involve the clouding of the eye’s lens, leading to vision impairment. This condition can be congenital or develop with age. Diabetic dogs are also prone to cataracts. Surgical intervention may be necessary for advanced cases.
- Glaucoma: Glaucoma is characterized by increased pressure within the eye, potentially leading to optic nerve damage and vision loss. Symptoms include redness, pain, dilated pupils, and cloudy corneas. Immediate veterinary attention is essential to manage glaucoma.
- Entropion and Ectropion: Entropion occurs when the eyelid rolls inward, causing the hair to rub against the cornea. Ectropion, on the other hand, involves the eyelid rolling outward. Both conditions can lead to irritation and corneal damage, often requiring surgical correction.
- Dry Eye (Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca): Dry eye results from inadequate tear production, leading to dryness, redness, and discomfort. This condition can be caused by autoimmune disorders or certain medications. Treatment involves artificial tears and medications to stimulate tear production.
Recognizing Symptoms of Ocular Issues
- Squinting or Blinking Excessively: Dogs experiencing pain or discomfort may squint or blink excessively. This behavior is often indicative of an underlying ocular problem.
- Redness and Inflammation: Inflammation of the eyes, characterized by redness, swelling, or a visible third eyelid, may signal various eye conditions, including conjunctivitis or cherry eye.
- Discharge: Abnormal eye discharge, whether clear, mucous-like, or purulent, can indicate infection or inflammation. The type and color of discharge can provide clues to the underlying issue.
- Cloudiness or Changes in the Eye’s Appearance: Cloudiness, opacity, or changes in the eye’s appearance may suggest cataracts, corneal ulcers, or other structural issues. Prompt veterinary evaluation is crucial for an accurate diagnosis.
- Rubbing or Pawing at the Eyes: Dogs may rub or paw at their eyes when experiencing discomfort. This behavior can exacerbate the problem and should prompt immediate attention.
- Changes in Pupil Size: Uneven or abnormal changes in pupil size could be a sign of glaucoma or other serious conditions affecting the eye. Seek veterinary care promptly if you notice irregularities.
Treatment Strategies for Ocular Issues
- Consultation with a Veterinarian: If you notice any signs of ocular issues in your dog, schedule a prompt consultation with a veterinarian. Professional assessment is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
- Prescription Medications: Depending on the diagnosis, your veterinarian may prescribe topical or oral medications, such as antibiotics, anti-inflammatories, or artificial tears, to address specific eye conditions.
- Surgical Interventions: Some ocular issues, like corneal ulcers, entropion, or cherry eye, may require surgical correction. Veterinarians can discuss the potential benefits and risks associated with surgical interventions.
- Management of Underlying Conditions: If ocular problems result from underlying health conditions, such as diabetes or autoimmune disorders, managing the primary issue is essential for comprehensive care.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: In cases of chronic conditions like dry eye, lifestyle adjustments may be necessary. This could include using humidifiers, providing a balanced diet, or administering medications as prescribed.
- Regular Veterinary Check-ups: Routine veterinary check-ups are crucial for monitoring your dog’s ocular health, especially for senior dogs or those prone to certain eye problems. Early detection allows for timely intervention.
- Preventive Measures: Some ocular issues can be prevented through proactive measures, such as regular grooming to prevent hair from irritating the eyes, avoiding trauma, and providing a well-balanced diet.

Holistic Approach to Ocular Health in Dogs
- Nutritional Support: Provide a balanced and nutritionally complete diet to support overall health, including ocular health. Consider incorporating foods rich in antioxidants, such as fruits and vegetables.
- Supplements for Eye Health: Consult with your veterinarian about supplements that promote eye health, such as those containing omega-3 fatty acids, lutein, and zeaxanthin.
- Environmental Considerations: Create an environment that minimizes potential eye irritants, such as dust, smoke, or harsh chemicals. Regular grooming can also prevent hair from causing ocular issues.
- Regular Exercise: Regular exercise promotes overall health and can contribute to better blood circulation, which is beneficial for ocular health.
- Maintain a Stress-Free Environment: Minimize stressors in your dog’s environment, as stress can impact overall health, including ocular health. Provide a calm and nurturing atmosphere at home.
- Educate Yourself: Stay informed about your dog’s breed-specific predispositions to certain eye problems. Awareness enables you to take preventive measures and seek prompt veterinary attention when needed.
Conclusion: Nurturing Canine Ocular Health
Caring for your dog’s eyes is an integral part of responsible pet ownership. By staying vigilant, recognizing signs of ocular issues, and taking a proactive and holistic approach to their well-being, you can contribute to maintaining your canine companion’s bright and healthy eyes. Always consult with your veterinarian for personalized guidance tailored to your dog’s specific needs.
As a dedicated dog owner, your commitment to ocular health fosters a deeper connection with your furry friend, ensuring they experience the world with clarity and comfort. Together, let’s embark on a journey toward preserving the vision and overall ocular health of our beloved canine companions.