Spaying or neutering your pet cat, whether male or female, offers various benefits, contributing to the well-being of the cat and addressing broader concerns related to pet overpopulation. Here are some reasons to consider spaying or neutering your cat:
Neutering (for males) and spaying (for females) are common surgical procedures performed on cats for population control and health reasons. These procedures offer several benefits for both the individual cat and the overall feline population:
Benefits of Neutering (Males):
- Population Control: Prevents the cat from contributing to the overpopulation of stray and feral cats.
- Behavioral Benefits: Reduces the likelihood of roaming and aggression, making male cats more likely to stay close to home and less prone to territorial disputes.
- Marking and Spraying Prevention: Reduces the urge to mark territory by spraying strong-smelling urine.
- Prevention of Testicular Diseases: Eliminates the risk of testicular tumors and reduces the likelihood of certain infections.
Benefits of Spaying (Females):
- Population Control: Prevents the cat from contributing to the overpopulation problem by eliminating the potential for unwanted litters.
- Prevention of Estrus-Related Behaviors: Eliminates or reduces behaviors associated with the estrus (heat) cycle, such as yowling, restlessness, and attracting male cats.
- Prevention of Unwanted Pregnancies: Ensures that female cats do not become pregnant, preventing the challenges and responsibilities associated with unwanted litters.
- Reduced Risk of Mammary Tumors: Spaying before the first heat significantly reduces the risk of mammary tumors, particularly if performed early in a cat’s life.
- Prevention of Uterine Infections: Eliminates the risk of uterine infections (pyometra), a potentially life-threatening condition.
General Benefits for Both Neutering and Spaying:
- Behavioral Improvement: Reduces undesirable behaviors such as roaming, aggression, and the instinct to mate, leading to a more predictable and manageable temperament.
- Health Benefits: Reduces the risk of certain reproductive-related cancers and infections.
- Promotes Responsible Pet Ownership: Encourages responsible pet ownership by preventing unplanned litters and helping control the cat population.
- Cost-Effective: Neutering and spaying are generally cost-effective compared to the potential costs associated with caring for a litter of kittens or addressing health issues related to reproductive organs.
It’s important to note that the timing of neutering and spaying can impact the associated benefits. Many veterinarians recommend performing these procedures before the cat reaches sexual maturity to maximize the health and behavioral advantages. Discussing the best timing for these procedures with a veterinarian is crucial for addressing the individual needs of each cat.
The behavior of cats after spaying (females) or neutering (males) can be influenced by a variety of factors, including the cat’s age, personality, and individual experiences. In general, spaying and neutering can have positive effects on a cat’s behavior, although the specific changes can vary. Here are common behavioral changes associated with spaying and neutering:
Females (After Spaying):
- Reduced Estrus-Related Behaviors: Spayed females typically no longer experience heat cycles, eliminating behaviors such as yowling, restlessness, and increased affection-seeking associated with mating behaviors.
- Decreased Aggression: Spaying can reduce aggression related to competition for mates, making female cats more sociable and less prone to territorial disputes.
- Lowered Risk of Roaming: Spayed females are less likely to roam in search of mates, leading to a reduced risk of outdoor dangers and decreasing the chances of unwanted pregnancies.
- Elimination of Pregnancy-Related Stress: The stress associated with pregnancies and raising kittens is eliminated, contributing to a more relaxed and content demeanor.
- Reduced Marking and Spraying: Spaying reduces the likelihood of urine marking and spraying, behaviors associated with the desire to attract mates.
Males (After Neutering):
- Reduced Roaming and Aggression: Neutered males are less likely to roam in search of mates and exhibit aggressive behaviors, making them more amenable to living in multi-cat households.
- Decreased Marking and Spraying: Neutering reduces the urge to mark territory by spraying strong-smelling urine, helping to maintain a cleaner and more odor-free environment.
- Lowered Risk of Fighting: Neutered males are less likely to engage in territorial disputes and fights with other males, reducing the risk of injuries and infections.
- Altered Sexual Behaviors: Neutering eliminates or significantly reduces behaviors associated with mating, such as mounting and excessive vocalization.
General Considerations:
- Recovery Period: Cats may exhibit temporary changes in behavior immediately after surgery due to the recovery process. Some cats may be more lethargic, while others may be more subdued or seek extra attention.
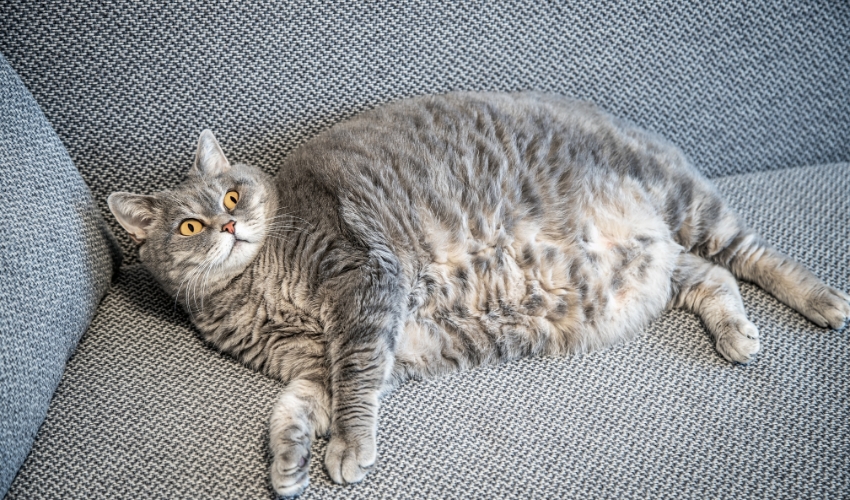
- Potential Weight Gain: Spayed and neutered cats may have a slightly lower metabolism, so it’s important to monitor their diet and activity levels to prevent weight gain.
- Individual Variation: The impact of spaying and neutering on behavior can vary from one cat to another. Individual factors, such as genetics and early life experiences, also play a role.
It’s important to note that spaying and neutering are recommended not only for behavioral reasons but also for the prevention of certain health issues and to contribute to responsible pet ownership. If you have specific concerns about your cat’s behavior after spaying or neutering, consulting with a veterinarian can provide guidance tailored to your individual cat’s needs.