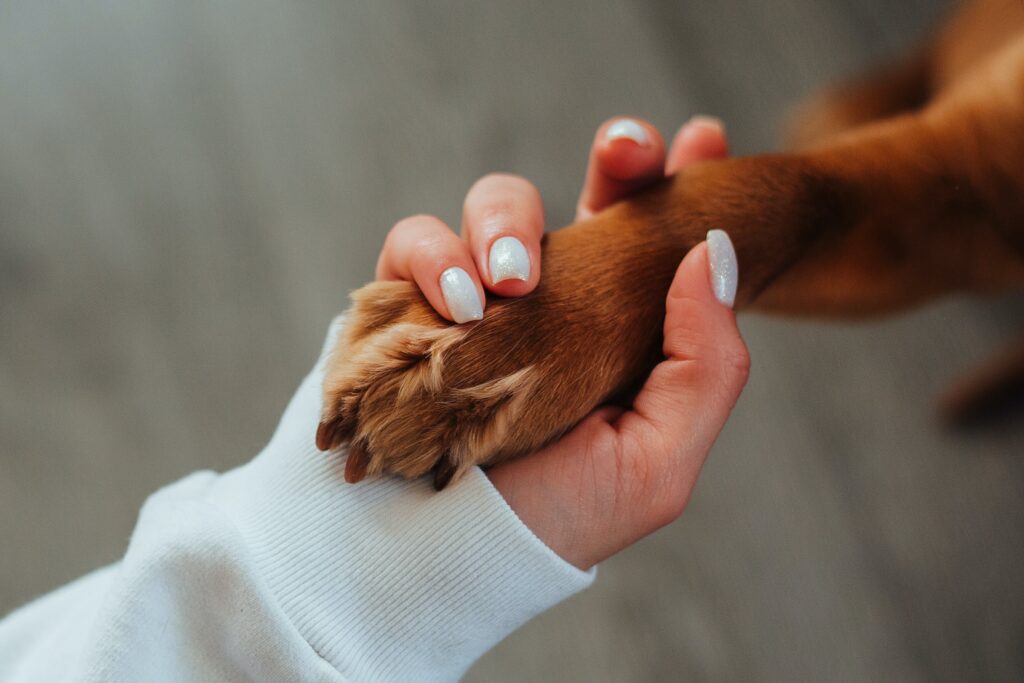
As devoted pet owners, we often find ourselves captivated by our canine companions’ fascinating behaviors and gestures. From the wag of their tail to the tilt of their head, dogs communicate with us through a language that extends far beyond barks and whines. In this comprehensive guide, we dive deep into the world of canine body language, providing invaluable insights into what our canine companions’ are trying to tell us.
Understanding your canine companion’s body language is essential for effective communication and building a strong bond with your furry friend. By deciphering their subtle cues and signals, we can gain a deeper understanding of their emotions, desires and also their needs. Our canine companions’ use a combination of postures, facial expressions, and vocalizations to convey their emotions and intentions. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the basics of dog body language, decode their emotional states, learn how to communicate, interact with humans and read their body language in specific situations. By the end of this guide, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge needed to interpret your dog’s body language and foster a deeper connection with them.
Understanding The Basics of Dog Body Language
Understanding the emotional states of dogs is essential for building a strong bond with your canine companion and ensuring their well-being. Dogs experience a wide range of emotions, similar to humans, and they communicate these feelings through their body language, behavior, and vocalizations. Here are some key emotional states of dogs and how to recognize them:
Happiness:
Signs of a happy dog include a relaxed body posture, loose tail wagging, soft and relaxed facial expressions, open mouth with a relaxed tongue, and playful behavior. Happy dogs may also exhibit affectionate gestures such as leaning against you or offering gentle nudges. Overall, a happy dog’s body language is characterized by relaxation. Playfulness, approachability, and contentment. By recognizing and responding to these cues, you can ensure your dog’s happiness and foster your bond with your canine companion.
Fear and Anxiety:
Fearful or anxious dogs may display signs such as trembling, panting excessively, pacing, hiding, cowering, tucking their tail between their legs, or attempting to escape. They may also exhibit avoidance behaviors, such as avoiding eye contact or backing away from perceived threats. It’s important to respond to your dog’s fear and anxiety with patience, understanding and compassion. Avoid punishing or scolding your dog for displaying fearful behavior, as this can exacerbate their anxiety and erode trust.
Stress:
Dogs can experience stress in various situations, such as during veterinary visits, loud noises, or changes in their environment. Signs of stress may include panting, drooling, excessive licking or chewing, yawning, whining, pacing, and shaking. Stress signals can escalate into more severe behaviors if not addressed promptly. It is important to respond to the with empathy and understanding. You can help them feel safe and secure by creating a calm environment and removing any potential stressors.
Aggression:
Aggression in dogs can stem from fear, frustration, territoriality, or resource guarding. Signs of aggression include growling, snarling, snapping, lunging, showing teeth, raised hackles, and stiff body posture. It’s essential to address aggressive behavior promptly and seek professional help if necessary. If you observe any signs of aggression in your dog, it’s crucial to address the issue promptly and seek professional help from a certified dog trainer or behaviorist.
Relaxation and Contentment:
Relaxed and contented dogs exhibit calm body language, such as lying down with their legs stretched out, resting their head on their paws, or sighing deeply. Their facial muscles are relaxed, with soft eyes and a slightly open mouth. Contented dogs may also exhibit gentle tail wags or relaxed ear positions.
Excitement:
Excited dogs may display high energy levels, such as jumping, spinning, or running in circles. Their tail may wag rapidly, and they may bark or vocalize enthusiastically. Excited dogs may also exhibit playful behavior, such as bringing you toys or engaging in sudden bursts of energy and running.
Loneliness and Boredom:
Dogs are social animals and can experience loneliness and boredom when left alone for extended periods. Signs of loneliness and boredom may include whining, excessive barking, destructive chewing or digging, pacing, and lethargy. Providing mental stimulation and companionship can help alleviate these feelings or spending time to play with them.
It’s essential to remember that each dog is an individual with their own unique personality and experiences. Pay attention to your dog’s body language, behavior, and vocalizations to better understand their emotional state and respond accordingly. If you’re unsure about your dog’s emotions or behavior, consult with a professional dog trainer or behaviorist for guidance and support.
How Dogs Use Body Language To Communicate With Humans
Dogs use body language as a primary means of communication with humans, conveying their emotions, needs, and intentions through a variety of gestures and signals. Understanding your canine companion’s body language can help strengthen your bond and improve communication between you and your furry friend. Here’s how dogs use body language to communicate with humans:
Tail Wagging:
Tail wagging is perhaps the most recognizable sign of a dog’s mood. A wagging tail can indicate happiness, excitement, or friendliness. However, the position and speed of the wag can convey different meanings. For example, a broad, loose wag often signifies a happy dog, while a stiff or fast wag may indicate agitation or arousal.
Facial Expressions:
Dogs use facial expressions to communicate a wide range of emotions. Relaxed facial muscles, soft eyes, and an open mouth with a relaxed tongue typically indicate a calm and contented dog. All the while, wide eyes with dilated pupils, raised eyebrows, or bared teeth may suggest fear, anxiety, or aggression in dogs.
Eye Contact:
Eye contact is an essential form of communication for dogs. A dog having or making a direct eye contact with you may be seeking for attention, affection, or guidance. However, prolonged staring or a fixed, intense gaze can be perceived as threatening or confrontational in dog language.


Ear Position:
Dogs use ear position to express their emotions and intentions. Erect ears generally indicate attentiveness or alertness, while flattened ears may signal fear, anxiety, or submission. One ear forward and one ear back may suggest curiosity or uncertainty.
Body Posture:
Your dog’s overall body posture provides valuable insights into their mood and intentions. A relaxed, loose stance with a slightly wagging tail typically indicates a happy and comfortable dog. Conversely, a tense, stiff body posture with raised hackles may signal fear, aggression, or arousal.
Vocalizations:
Dogs use a variety of vocalizations, including barks, growls, whines, and howls, to communicate with humans. The tone, pitch, and intensity of these vocalizations can convey different emotions and intentions. For example, a low, rumbling growl may indicate aggression or warning, while a high-pitched whine may signify anxiety or excitement.
Physical Contact:
Dogs often seek physical contact with humans as a form of communication and affection. They may lean against you, nuzzle your hand, or offer gentle nudges to solicit attention or express their bond with you.
By paying attention to your dog’s body language and cues, you can better understand their emotions and respond appropriately to their needs. Building a strong foundation of communication through body language enhances your relationship with your dog and fosters a deeper understanding and connection between you both.
Learning to understand your dog’s body language is an invaluable skill that will enhance your relationship and ensure effective communication. By observing their postures, facial expressions, and vocalizations, you’ll be able to decipher their emotions, needs, and intentions. Remember, each dog is unique, so pay attention to their individual body language cues and preferences. With the insights gained from this ultimate guide, you and your furry companion will embark on a journey of better understanding, trust, and deeper connection.