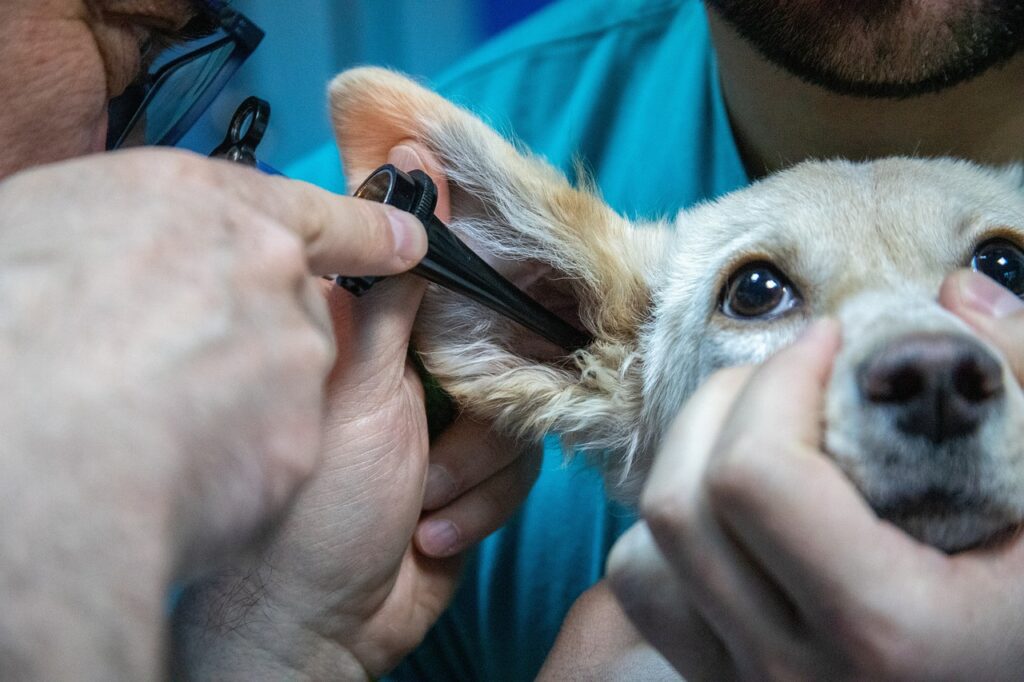
Our canine companions are susceptible to various health issues. In this guide, we’ll explore the top 10 most common medical problems in dogs. Understanding these conditions and their symptoms is essential for pet owners to ensure early detection, proper care, and the overall well-being of our furry friends.
- Ear Infections
Approximately 20 percent of dogs experience some form of ear disease, with the most common being otitis externa. In otitis externa, the lining of the external ear canal becomes inflamed, potentially affecting one or both ears. It can be caused by parasites, foreign objects, moisture and wax buildup, allergies or thyroid issues and autoimmune disorders. Should you notice any of these signs of an ear infection in your pooch, it’s crucial to promptly get in touch with your veterinarian:
- Head shaking
- Unpleasant odor
- Swelling
- Scratching
- Increased discharge
- Head tilting
- Crusting or scabs
- Skin Allergies
Skin allergies in doggos, known as allergic dermatitis, are prevalent and result from an overreaction of the immune system to specific allergens. These allergies typically stem from three main sources: food, environmental triggers, and fleas. Canine skin allergies may lead to a range of symptoms such as:
- Red or flakey skin
- Scooting or rubbing on surfaces
- Hives
- Hair loss
- Rubbing of face/ears
- Excessive scratching
- Excessive licking
- Chewing or biting the skin

- Gastrointestinal Issues
Gastrointestinal disorders and other digestive problems can lead to pain and discomfort in a dog’s stomach and intestines which are a frequent reason for our sniffers to visit the veterinarian. Digestive issues in canines are due to various reasons such as dietary indiscretion, stress, parasites, toxic ingestion, and infections to mention a few. Aside from diarrhea, you might also observe a combination of the following symptoms:
- Excessive drooling
- Constipation
- Increased gas
- Lack of appetite
- Fever
- Abdominal pain
- Abdominal enlargement
- Distress
- Straining to defecate
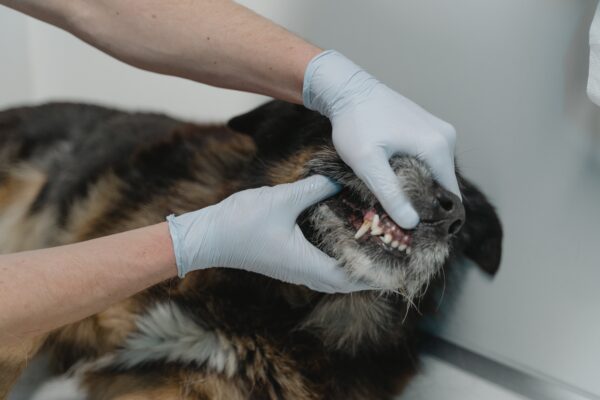
- Periodontal Disease
Periodontitis in our tail-wigglers is caused by bacteria infecting the oral cavity due to the accumulation of dental plaque and tartar on the teeth. It also can be influenced by factors such as diet, poor nutrition, grooming habits, dirty toys, teeth alignment, and oral hygiene. This leads to inflammation, resulting in chronic pain, gum erosion, and the potential loss of bone and teeth. The indications of dental problems in dogs include:
- Bleeding gums or bloody saliva
- Brown or yellow teeth
- Inability to chew hard food
- Favoring one side of the mouth when chewing
- Broken or missing teeth
- Bad breath
- Irritability
- Excessive drooling

- Orthopedic Issues
Orthopedic veterinary issues encompass diseases affecting various structures such as bones, tendons, ligaments, cartilage, and joints in dogs. These conditions commonly include cruciate ligament tears, hip or elbow dysplasia, luxated patella, and arthritis. The symptoms of orthopedic disorders in our furbabies can vary but often share common symptoms, including:
- Abnormal gait
- Irritability
- Lethargy
- Loss of appetite
- Misshapen limbs
- Stiffness
- Swelling of the joints
- Weight gain
- Obesity
Rovers exceeding 10% above their ideal weight are considered overweight, with those surpassing 20% classified as obese. Overfeeding and insufficient exercise are primary contributors to canine obesity, along with medical conditions such as hypothyroidism and hyperadrenocorticism. Obesity in our hounds is associated with various health issues, including arthritis, chronic kidney disease, urinary tract problems, liver disease, low thyroid hormone production, diabetes, heart failure, high blood pressure, and cancer. Signs of obesity include:
- Weight gain
- Lethargy
- Decreased exercise tolerance
- No palpable ribcage
- Distended abdomen
- Difficulty breathing
- Urinary Tract Infections
UTIs are common in dogs, especially females, and can be isolated or recurrent, particularly if a dog has underlying health issues. Bacterial UTIs, affecting 14% of dogs in their lifetime, are prevalent, especially in older canines aged 7 and above. When symptoms of UTI become apparent, they might manifest as follows:
- Straining to urinate
- Frequent urination
- Foul smelling urine
- Excessively licking genitals
- Bloody or cloudy urine
- Excessive drinking
- Lack of appetite
- Fever
- Lethargy
- Parasites
Pet owners should be mindful of two main categories of parasites in mutts: internal and external. Internal parasites like hookworms, roundworms, and tapeworms reside inside the body, potentially impacting various organs and transmitted through different means. External parasites, such as fleas and ticks, live on the host’s body, leading to infestations.
The symptoms of parasites may differ based on the specific type of parasite, its location, and the severity of the infestation.
External Parasites:
- Excessive scratching
- Hair shedding
- Scabbing
- Dull coat
- Black remnants in ears
- Fleas
- Agitated behavior


Internal Parasites:
- Diarrhea, with or without blood or mucous
- Retching or vomiting
- Poor appetite
- Swollen belly
- Lethargy
- Scooting
- Feces with worms or segments
- Coughing
- Labored breathing
- Eye Problems
Various ophthalmic conditions may affect our bark buddies at different life stages. These include corneal damage, dry eye, pink eye, eyelid mass, cataracts, glaucoma, cherry eye, and entropion. These conditions can arise at any time and may impact our woofer’s vision and overall ocular health.
Here are signs and symptoms to look for:
Corneal damage:
- redness and excessive tearing
- squints the eye closed
- pawing at the eye
Dry eye:
- Redness
- Squinting and blinking
- pawing at the eye
- Eye discharge
Pink eye:
- Green or yellow discharge
- Squinting or holding the eye closed
- Rubbing the eye
- Redness or inflammation
Eyelid mass:
- Bump on or at the edge of the eyelid
Cataracts:
- White or cloudy eyes
Glaucoma:
- Redness
- Tearing
- visible vessels on the whites of the eye
- Bulging and dilated pupil
- Cloudy cornea
Cherry eye:
- Inflamed eyelid resembling a cherry
Entropion:
- Swollen eyes
- Squinting
- Excessive tearing
- Cancer
Cancer is prevalent in our senior buddies, with over 50% of those aged 10 and above are affected. The most common types include skin cancers such as melanomas and mast cell tumors, as well as lymphomas and bone cancers. Seek advice from your veterinarian if you notice any of the following signs in your pet:
- Bleeding from the mouth, nose or other body openings
- Difficulty breathing
- Difficulty swallowing
- Lumps and bumps underneath skin
- Non-healing wounds
- Weight loss
- Unexplained swelling, heat, pain or lameness
It’s essential to provide proper veterinary care, a balanced diet, regular exercise, and a clean living environment to help prevent and manage these conditions.